What if the future of coding wasn’t just about human ingenuity but also about the battle of AI giants? Imagine two innovative AI models OpenAI’s GPT-5 and Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet competing to build a multiplayer tic-tac-toe game. One delivers deliberate, rule-abiding solutions, while the other dazzles with speed and visual finesse. Yet, neither emerges flawless. This isn’t just a tech showdown; it’s a glimpse into how AI shapes the tools we use to solve problems, design interfaces, and even manage costs. As developers increasingly rely on AI for coding tasks, the stakes have never been higher: which model truly delivers the edge?
In this comparison , Convex breaks down the strengths, weaknesses, and surprising quirks of GPT-5 and Claude Sonnet. From token efficiency and pricing to their ability to handle complex tasks like authentication, you’ll discover how these models stack up in real-world scenarios. Whether you’re a developer seeking precision or speed, or just curious about how AI models differ in their approach to problem-solving, this comparison will help you navigate the trade-offs. By the end, you might find yourself questioning not just which model is better—but what “better” really means in the evolving landscape of AI-driven development.
GPT 5 vs Claude Sonnet
TL;DR Key Takeaways :
- GPT-5 excels in advanced reasoning and deliberate problem-solving, producing high-quality outputs but with slower processing and higher token usage.
- Claude Sonnet offers faster execution and visually polished results, though it struggles with schema consistency and occasionally produces incomplete solutions.
- Both models faced challenges in authentication tasks, requiring manual intervention for issues like environment variable management and TypeScript compatibility.
- GPT-5 is more token-intensive and costly but provides detailed and accurate outputs, while Claude Sonnet is more cost-efficient for simpler, speed-focused tasks.
- The choice between GPT-5 and Claude Sonnet depends on project priorities: GPT-5 for accuracy and complexity, and Claude Sonnet for speed and visual appeal.
Key Features of ChatGPT 5 and Claude Sonnet
GPT-5, OpenAI’s latest offering, is engineered for advanced reasoning and adaptability across diverse challenges. It employs a routing mechanism to optimize task performance, making it a versatile tool for developers. Claude Sonnet, a competing model, is recognized for its speed and visually refined outputs, catering to developers who prioritize efficiency and design aesthetics. While both models aim to assist in coding and problem-solving, their approaches and results differ significantly.
Performance in Building a Multiplayer Tic-Tac-Toe Game
To evaluate their coding capabilities, both models were tasked with creating a multiplayer tic-tac-toe game. The results highlighted distinct strengths and weaknesses:
- GPT-5: Delivered a functional and robust solution, though its interface was visually basic and required additional design work.
- Claude Sonnet: Produced a polished and visually appealing interface but occasionally included unnecessary schema fields, complicating the codebase.
Both models encountered minor coding errors and redundant schema elements, emphasizing the importance of manual refinement regardless of the model used. These findings suggest that while both tools are capable, neither can fully replace human oversight in development tasks.
Impact of Rule Adherence on Model Performance
The ability to follow structured requirements, such as cursor guidelines and schema conventions, was tested to assess how rules influence performance. The models exhibited contrasting behaviors:
- GPT-5: Demonstrated slower but more deliberate processing, often providing thoughtful and detailed solutions that adhered closely to the rules.
- Claude Sonnet: Executed tasks more quickly but struggled with schema conventions and index handling, leading to occasional inconsistencies in its outputs.
These differences highlight how each model’s inherent processing style affects its ability to meet structured requirements. While rules can improve performance, the quality of outputs depends heavily on the model’s internal logic and reasoning capabilities.
Challenges in Authentication Implementation
Authentication tasks, such as implementing username/password and anonymous login systems, posed significant challenges for both models. The results revealed key insights:
- Both models faced difficulties with environment variable management and TypeScript compatibility, requiring additional manual intervention to resolve issues.
- GPT-5: Used web searches to compensate for its slower processing speed, often resulting in more complete and reliable solutions.
- Claude Sonnet: Executed tasks quickly but occasionally produced incomplete or less dependable functions, requiring further debugging.
These findings underscore the complexity of authentication tasks and the need for developers to carefully review and refine outputs, regardless of the model used.
Token Efficiency and Cost Implications
Token efficiency is a critical factor in determining the cost-effectiveness of AI models. The comparison revealed distinct patterns in token usage:
- GPT-5: Consumed more tokens due to its extensive reasoning process, often resulting in higher-quality outputs. Despite using more tokens, its lower per-token rates can make it cost-competitive, especially for complex projects where accuracy is essential.
- Claude Sonnet: Used fewer tokens but relied heavily on its context window, particularly when rules were not explicitly defined. However, its higher per-token rates can offset the savings from reduced usage.
These differences highlight the trade-offs between reasoning depth and token efficiency. GPT-5 offers strong value for detailed, accuracy-driven work, while Claude Sonnet may be better suited for tasks that emphasize speed and brevity.
Pricing and Cost Analysis
Cost is a significant consideration when selecting an AI model. The pricing structures for GPT-5 and Claude Sonnet are as follows:
- GPT-5: $1.25 per million input tokens and $10 per million output tokens.
- Claude Sonnet: $3 per million input tokens and $15 per million output tokens.
While GPT-5 is more affordable on a per-token basis, Claude Sonnet’s lower overall token usage may still make it competitive for shorter, more focused tasks. The choice between the two models should align with your project’s specific budget and requirements.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Model
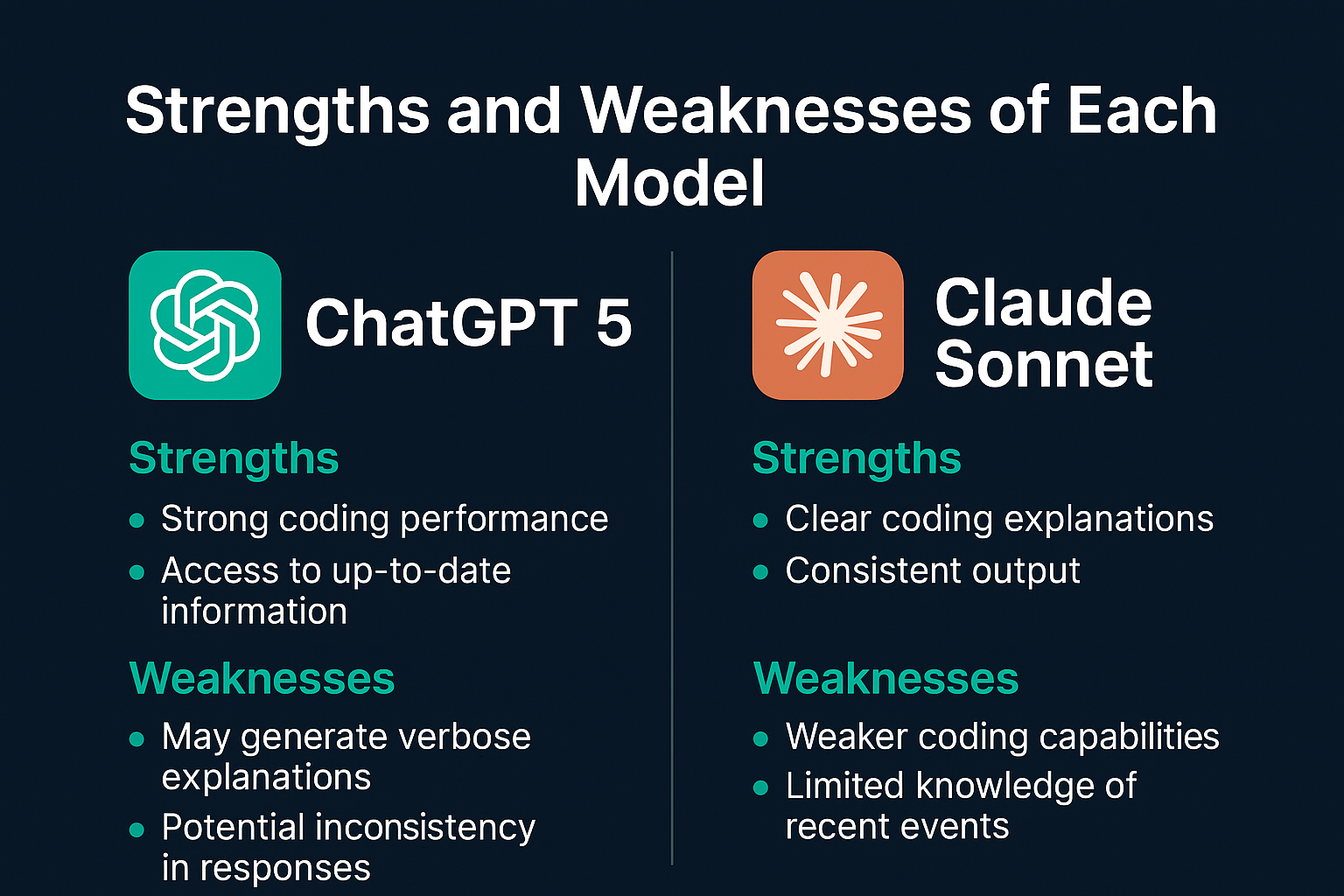
The comparison highlights distinct strengths and weaknesses for GPT-5 and Claude Sonnet, making them suitable for different use cases:
- GPT-5:
- Strengths: Advanced reasoning, deliberate problem-solving, and high-quality outputs.
- Weaknesses: Slower processing, higher token usage, and occasional errors in execution.
- Claude Sonnet:
- Strengths: Faster execution, visually appealing outputs, and efficient token usage.
- Weaknesses: Inconsistent schema handling, less reliable methods, and occasional incomplete solutions.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Needs
Both GPT-5 and Claude Sonnet offer unique advantages, making them suitable for different types of projects. GPT-5 excels in tasks that require complex problem-solving and reasoning, though its slower processing and higher token usage may be drawbacks for time-sensitive projects. Claude Sonnet, on the other hand, provides faster execution and visually polished results but struggles with consistency and schema handling.
Your choice should depend on your project’s specific needs. If accuracy, reasoning, and detailed outputs are priorities, GPT-5 may be the better option. For tasks that demand speed and visual appeal, Claude Sonnet could be more suitable. As both models continue to evolve, ongoing testing and updates will provide deeper insights into their capabilities, allowing developers to make even more informed decisions in the future.